A Simple Guide to K-Nearest Neighbor Classification using Python
Python | Machine Learning | Algorithm | K-Nearest Neighbour | Project
Hello, All.
This is my first article on Hashnode. Feeling nervous to try something new. I hope this will be best decision taken. I'll be sharing all my learnings and knowledge I've gained on Machine Learning in my new series titled "Machine Learning".
Let's get started without any delay.
👇Introduction
This article is basically concerned with Supervised ML Classification Algorithm-KNN (K Nearest Neigbors) algorithm. It's one of the easy and mostly used classification algorithms where a new data point is differentiated based on resemblance in the particular group of neighboring data points. It provides a competitive result.
💻How it works?
The algorithm checks the distances between this and every other K numbers of datapoint from the dataset whch are close to the initial point and selects that group which has better frequency for a given data point in the set. Generally, Euclidean distance is considered as measure of distance. The end model result is the labelled data set in space. This algorithm is famously known for wide range of applications such as genetics, forecasting etc. This is used best when added features are present and out displays SVM algorithm in this case.
The fact is KNN reduces overfitting. On the other hand, we have a requirement to choose the best value for K. So how can we choose K value? Usually, we take the square root of number of samples in dataset as value for defining K. The optimal value should be found out as lower value might lead to overfitting and higher value might need larger computational complication in distance. So usage of error plot might help. Other method we have got is elbow method. Root can be taken preferrably else elbow method can be followed.
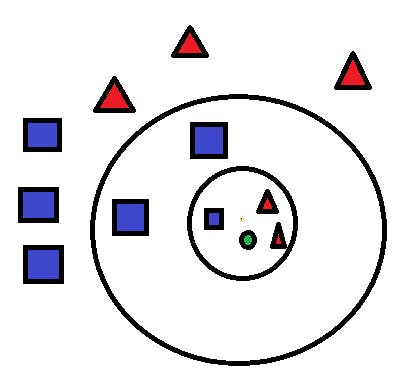
🚀Approach
Let's indulge deep into the different steps of K-NN involved in categorizing a new data point.
Step 1: Pick the value of K neighbors(let's say K=5) Step 2: Based on euclidean distance, search the K (5) nearest data point for our new data point Step 3: From all these K data points sum up the data points in every single category Step 4: Allocate the new data point to the category which has the better nearest neighbors of the new datapoint
Example
Let’s get it started through an example problem for getting a clear instinct on the K-Nearest Neighbor classification. To solve this problem, we will be using the Social Network Ad Dataset. This dataset holds the users details from social networking site to know whether a user would buy a product by clicking the ad from the site depending on their salary, age and gender.
We will start our programming through importing essential libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import sklearn
Dataset is imported and sliced into independent and dependent variables
dataset = pd.read_csv('Social_Network_Ads.csv')
X = dataset.iloc[:, [1, 2, 3]].values
y = dataset.iloc[:, -1].values
We have to encode using LabelEncoder as our dataset contains character variables
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
le = LabelEncoder()
X[:,0] = le.fit_transform(X[:,0])
The train_test_split is performed on the dataset. We are giving the test size to be 0.20 which means that our training sample would contain 320 training set and test sample would contain 80 test sets.
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.20, random_state = 0)
Now, we will do feature scaling to the training set and testing set of independent variables to reduce the size of smaller values
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
sc = StandardScaler()
X_train = sc.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = sc.transform(X_test)
Then, we should create and train the KNN Model with the training set available
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
classifier = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = 5, p = 2, metric = 'minkowski')
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
In model creation, we are using 3 parameters. n_neighbors is set to 5, which says that 5 nearest neighborhood points are required for categorizing a given point. We will be using Minkowski distance metric here and equation for it is shown below :
n
(∑|xi-yi|p)1/p
i=1
From the equation, p-value should have to be selected as well.
p = infinity , Cheybchev Distance /
p = 1 , Manhattan Distance /
p = 2 , Euclidean Distance
For our problem, we are selecting the p as 2 (you can choose the metric as "euclidean" as well) We have created our model, now we will the predicting the output for the test set
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
Differentiating true and predicted value :
y_test
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,
0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0,
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1,
0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1,
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1], dtype=int64)
y_pred
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,
0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0,
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1,
0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1], dtype=int64)
Model can be evaluated using the confusion matrix and accuracy score by differentiating the predicted and actual test values
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix,accuracy_score
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
ac = accuracy_score(y_test,y_pred)
Confusion matrix
[[64 4]
[ 3 29]]
Accuracy is 0.95
We can now see that our model is performing good. The entire code to this problem is shown below :
# Importing the libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
# Importing the dataset
dataset = pd.read_csv('Social_Network_Ads.csv')
X = dataset.iloc[:, [2, 3]].values
y = dataset.iloc[:, -1].values
# Splitting the dataset into the Training set and Test set
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.20, random_state = 0)
# Feature Scaling
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
sc = StandardScaler()
X_train = sc.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = sc.transform(X_test)
# Training the K-NN model on the Training set
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
classifier = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = 5, metric = 'minkowski', p = 2)
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Predicting the Test set results
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
# Making the Confusion Matrix
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, accuracy_score
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
ac = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
📫Conclusion
Now you know the what is K-Nearest Neighbor Algorithm and the concept is covered. You can implement and get used to it with different datasets available and get familiar with this algorithm. Experimenting can be done with values of p and n_neighbors. The ratio of train_test_split data can vary as well but it's recommended to 80:20 ratio for beginers as it would indeed be a good starting point to differentiate with various algorithms. Hope it was useful and gave a quick insight to K-Nearest Neighbor Classification using Python.
You can visit Kaggle to find more datasets that you can perform Classification with K-Nearest Neighbors.
I hope you found this article helpful. Drop me your comments, like and do share your valuable opinions, if it did. Also I would be happy to know about how you felt working on KNN Classification for the very first time.
Thanks for reading. I would love to connect with you at LinkedIn | Twitter.🤝🏻
📖You should definitely check out my other Blogs:
See you in my next article, Take care.
GOOD LUCK 👍
